You can use audit logging in on-premises Exchange Server and cloud-based Exchange Online (Microsoft 365) to track all user actions on any items in a mailbox. By using mailbox activity auditing, an Exchange administrator can easily answer the popular question “How to find out a user who deleted an email from a shared mailbox?”
In this article, we’ll show you how to enable and configure audit logging in Exchange Server and Microsoft 365 mailbox and how to review audit logs.
Enable Audit Logging in Office 365 (Microsoft 365) Mailboxes
First of all, let’s look at the audit features in Microsoft 365 tenant mailboxes. They are available only for E3- and E5-level subscribers.
Open PowerShell and connect to your Exchange online using the EXOv2 module:
Connect-ExchangeOnline -UserPrincipalName [email protected] -ShowProgress $true
The audit logging is enabled by default in Exchange Online (Office 365) for all tenants since late 2018.
Get-OrganizationConfig | Format-List AuditDisabled
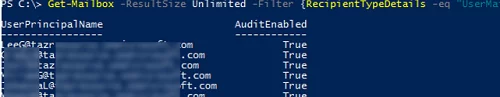
You can enable/disable the audit in the settings of each mailbox. Let’s display the current audit settings for all mailboxes:
Get-Mailbox -ResultSize Unlimited -Filter {RecipientTypeDetails -eq "UserMailbox"} | Select UserPrincipalName,AuditEnabled
As you can see, the audit is enabled. You can disable auditing for a specific mailbox:
Set-Mailbox maxbak -AuditEnabled $false
The Exchange allows using the following levels of mailbox activity auditing
- AuditOwner –audit owner actions;
- AuditAdmin –audit administrator actions;
- AuditDelegate –audit actions of other users who have been granted access to the mailbox.
The following events may be registered in the audit log:
- Copy
- Create
- FolderBind
- HardDelete
- MailboxLogin
- MessageBind
- Move
- MoveToDeletedItems
- SendAs
- SendOnBehalf
- SoftDelete
- Update
- UpdateCalendarDelegation
- UpdateFolderPermissions
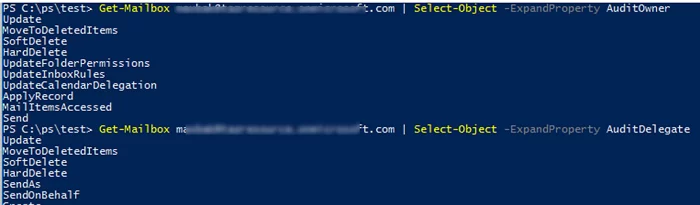
For each audit level, you can configure the events that should be logged. You can get current audit settings using these commands:
Get-Mailbox maxbak| Select-Object -ExpandProperty AuditOwner
Get-Mailbox maxbak| Select-Object -ExpandProperty AuditDelegate
Get-Mailbox maxbak| Select-Object -ExpandProperty AuditAdmin
You can configure only certain types of events to be registered in the log. For example, to audit item removal events:
Set-Mailbox maxbak -AuditOwner HardDelete,SoftDelete
If you only want to add other audit events to the existing ones:
Set-Mailbox maxbak -AuditOwner @{Add=”MailboxLogin”,”HardDelete”}
Audit logs are stored directly in the Audits folder of each mailbox. The folder is unavailable from Outlook or OWA.
You can get the current audit log size in a mailbox using the command below:
Get-MailboxFolderStatistics -Identity [email protected] | where {$_.FolderType -eq 'Audits'} | ft Identity, ItemsInFolder, FolderSize –auto
How to Enable Mailbox Audit Logging in Exchange Server?
In on-prem Exchange Server, mailbox audit is available in 2010 SP1+. By default, the mailbox audit is disabled.
Connect to your on-prem Exchange Server using PowerShell:
$Session = New-PSSession -ConfigurationName Microsoft.Exchange -ConnectionUri http://mun-mbx01.woshub.com/PowerShell/ -Authentication Kerberos -Credential $UserCredential
Import-PSSession $Session
You can enable audit logging for a single mailbox:
Set-Mailbox maxbak -AuditEnabled $true
Or for all mailboxes in your Exchange organization:
Get-Mailbox -ResultSize Unlimited -Filter {RecipientTypeDetails -eq "UserMailbox"} | Set-Mailbox -AuditEnabled $true
In Exchange Server mailboxes, administrator and delegate actions are audited (the default settings differ from those in Exchange Online). Owner activity auditing is disabled. If you enable an audit of all events of a mailbox owner, the log size will grow much faster. It is better to enable selective auditing of some actions (for example, deleting or moving):
Set-Mailbox maxbak -AuditOwner SoftDelete,HardDelete,MoveToDeletedItems,Move
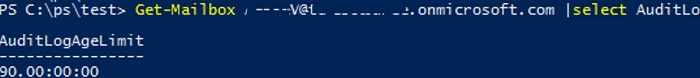
Audit events are stored for 90 days and deleted afterward. You can manage audit log depth (and size). For example, you can reduce the retention period for events in a mailbox from 90 to 30 days:
Get-Mailbox maxbak |select AuditLogAgeLimit
Set-Mailbox maxbak -AuditLogAgeLimit 30 -Force
Find Out Who Deleted an Email from a Shared Exchange Mailbox
Suppose, there is a shared mailbox in your Exchange tenant/organization accessible by other users. One of the users deleted an important email and you need to find out who did it.
To search mailbox audit logs, the Search-MailboxAuditLog cmdlet is used. The cmdlet is available both in on-prem Exchange Server and in cloud Exchange Online (some options may differ).
The following command displays all item activity (audit log) on a specific shared mailbox since February 1:
Search-MailboxAuditLog -Identity [email protected] -StartDate 2/1/2022 -ShowDetails| ft MailboxOwnerUPN, LogonType, LogonUserDisplayName, Operation,OperationResult, SourceItemSubjectsList,FolderPathName, DestFolderPathName,LastAccessed|ft
The search may take quite a long time depending on the number of audit events. The image shows who has deleted an email with the specified subject (the MoveToDeleteItems user action).
You can apply detailed filters to your audit logs. For example, you want to select delete events only (HardDelete, SoftDelete, MoveToDeletedItems) related to non-owner users:
Search-MailboxAuditLog -Identity support [email protected] -StartDate 2/2/2022 -EndDate 2/8/2022 –LogonTypes Delegate,Admin -ShowDetails| Where-Object {$_.Operation -like "*Delete*"}|ft MailboxOwnerUPN, LogonType,LogonUserDisplayName,Operation, OperationResult,SourceItemSubjectsList,FolderPathName, DestFolderPathName,LastAccessed|ft
To perform an asynchronous search for audit events, the New-MailboxAuditLogSearch cmdlet is used. It causes less load on the mailbox server, runs in the background, allows you to find the information you want among thousands of events effectively, and sends results to the specified mailbox.
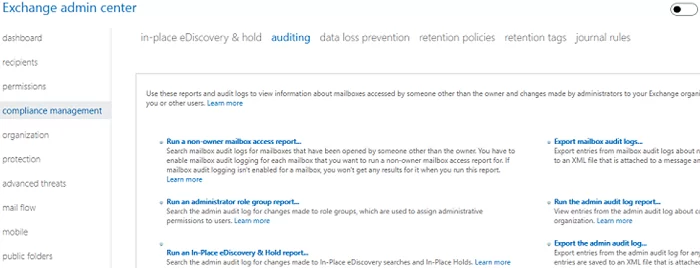
You can also search audit logs in Compliance Management -> Auditing of the Exchange Admin Center (EAC). You can use the “Run a non-owner mailbox access report” or “Export mailbox audit logs” options.
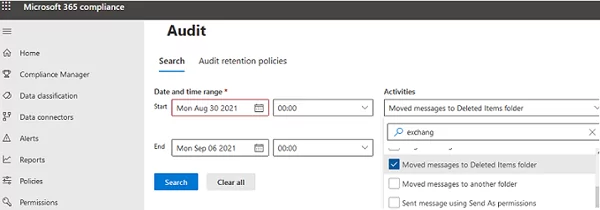
In Exchange Online, you can use either the EAC (a legacy way) or Microsoft 365 Compliance Center (https://compliance.microsoft.com/homepage) to search the audit logs. To search for event, go to Solutions -> Audit -> Search. Select a time period, choose “Moved messages to Deleted Items folder”, “Deleted messages from Deleted Items folder”.
Search-UnifiedAuditLog cmdlet.Also, you can use Exchange audit events to check if an email has been read by the recipient.