The Server Message Block (SMB) network protocol is used to share and access folders, files, printers, and other devices over network (TCP port 445). In this article, we will look at which versions (dialects) of SMB are available in different versions of Windows (and how they relate to samba versions on Linux); how to check the SMB version in use on your computer; and how to enable or disable the SMBv1, SMBv2, and SMBv3 dialects.
SMB Protocol Versions in Windows
There are several versions of the SMB protocol (dialects) that have consistently appeared in new Windows versions (and samba) :
- CIFS – Windows NT 4.0
- SMB 1.0 – Windows 2000
- SMB 2.0 – Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista SP1 (supported in Samba 3.6)
- SMB 2.1 – Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7 (Samba 4.0)
- SMB 3.0 – Windows Server 2012 and Windows 8 (Samba 4.2)
- SMB 3.02 – Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows 8.1 (not supported in Samba)
- SMB 3.1.1 – Windows Server 2016 and Windows 10 (not supported in Samba)
In SMB network communication, the client and server use the maximum SMB protocol version supported by both the client and the server.
The summary table of SMB version compatibility looks like this. Using this table, you can determine the version of the SMB protocol that is selected when different versions of Windows interact:
| Operating System | Windows 10, Win Server 2016 | Windows 8.1, Win Server 2012 R2 | Windows 8,Server 2012 | Windows 7,Server 2008 R2 | Windows Vista,Server 2008 | Windows XP, Server 2003 and earlier |
| Windows 10, Windows Server 2016 | SMB 3.1.1 | SMB 3.02 | SMB 3.0 | SMB 2.1 | SMB 2.0 | SMB 1.0 |
| Windows 8.1, Server 2012 R2 | SMB 3.02 | SMB 3.02 | SMB 3.0 | SMB 2.1 | SMB 2.0 | SMB 1.0 |
| Windows 8, Server 2012 | SMB 3.0 | SMB 3.0 | SMB 3.0 | SMB 2.1 | SMB 2.0 | SMB 1.0 |
| Windows 7, Server 2008 R2 | SMB 2.1 | SMB 2.1 | SMB 2.1 | SMB 2.1 | SMB 2.0 | SMB 1.0 |
| Windows Vista, Server 2008 | SMB 2.0 | SMB 2.0 | SMB 2.0 | SMB 2.0 | SMB 2.0 | SMB 1.0 |
| Windows XP, 2003 and earlier | SMB 1.0 | SMB 1.0 | SMB 1.0 | SMB 1.0 | SMB 1.0 | SMB 1.0 |
For example, if a client computer running Windows 8.1 connects to a file server with Windows Server 2016, the SMB 3.0.2 protocol will be used.
According to the table, Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 can use only SMB 1.0 to access shared folders and files. The SMBv1 is disabled in newer versions of Windows Server (2012 R2/2016). So, if you are still using Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 devices on your network, they won’t be able to access shared folders on the file server running Windows Server 2016.
If Windows Server 2019/2016 with disabled SMB v1.0 is used as a domain controller, then Windows XP/Server 2003 clients won’t be able to access the SYSVOL and NETLOGON folders on domain controllers and authenticate with AD.
You may receive the following error when trying to connect to a shared folder on a file server with SMBv1 disabled:
The specified network name is no longer available
How to Check SMB Version on Windows?
Let’s look on how to find out which versions of the SMB are enabled on your Windows device.
On Windows 10/8.1 and Windows Server 2019/2016/2012R2, you can check the status of various dialects of the SMB protocol using PowerShell:
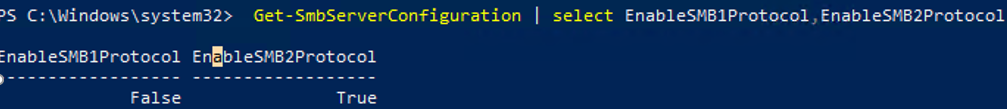
Get-SmbServerConfiguration | select EnableSMB1Protocol,EnableSMB2Protocol
This command returned that the SMB1 protocol is disabled (EnableSMB1Protocol = True), and the SMB2 and SMB3 protocols are enabled (EnableSMB1Protocol = False).
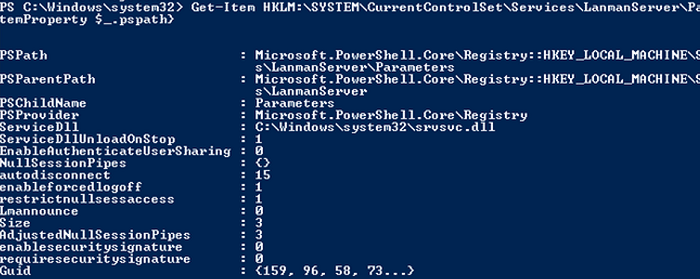
On Windows 7, Vista, and Windows Server 2008 R2/2008:
Get-Item HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters | ForEach-Object {Get-ItemProperty $_.pspath}
If there are no parameters named SMB1 or SMB2 in this registry key, then the SMBv1 and SMBv2 protocols are enabled by default.
Also on these Windows versions, you can check which SMB client dialects are allowed to connect to remote hosts:
sc.exe query mrxsmb10
SERVICE_NAME: mrxsmb10 TYPE : 2 FILE_SYSTEM_DRIVER STATE : 4 RUNNING (STOPPABLE, NOT_PAUSABLE, IGNORES_SHUTDOWN) WIN32_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0) SERVICE_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0) CHECKPOINT : 0x0 WAIT_HINT : 0x0
sc.exe query mrxsmb20
SERVICE_NAME: mrxsmb20 TYPE : 2 FILE_SYSTEM_DRIVER STATE : 4 RUNNING (STOPPABLE, NOT_PAUSABLE, IGNORES_SHUTDOWN) WIN32_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0) SERVICE_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0) CHECKPOINT : 0x0 WAIT_HINT : 0x0
In both cases, the services are running (STATE = 4 Running). This means that the current Windows device can connect to both SMBv1 and SMBv2 hosts.
Checking Used SMB Dialects with Get-SMBConnection
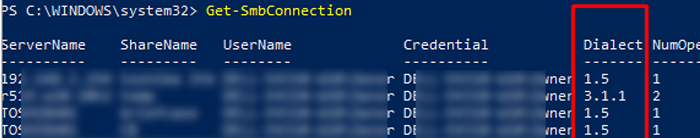
When communicating over SMB, computers use the maximum SMB version supported by both the client and the server. The Get-SMBConnection PowerShell cmdlet can be used to check the SMB version used to access a remote computer:
The SMB version used to connect to the remote server (ServerName) is listed in the Dialect column.
You can display information about the SMB versions used to access a specific server:
Get-SmbConnection -ServerName srvfs01
If you want to display if SMB encryption is in use (introduced in SMB 3.0):
Get-SmbConnection | ft ServerName,ShareName,Dialect,Encrypted,UserName
$ sudo smbstatus
On the Windows SMB server side, you can display a list of the versions of the SMB protocols that the clients are currently using. Run the command:
Get-SmbSession | Select-Object -ExpandProperty Dialect | Sort-Object -Unique
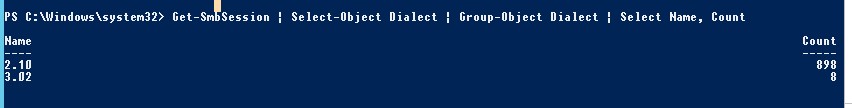
You can use PowerShell to enable auditing of the SMB versions used for the connection:
Set-SmbServerConfiguration –AuditSmb1Access $true
SMB connection events can then be exported from Event Viewer logs:
Get-WinEvent -LogName Microsoft-Windows-SMBServer/Audit
Stop Using the Insecure SMBv1 Protocol
Over the past few years, Microsoft has systematically disabled the legacy SMB 1.0 protocol in all products for security reasons. This is due to the large number of critical vulnerabilities in this protocol (remember the incidents with wannacrypt and petya ransomware, which exploited a vulnerability in the SMBv1 protocol). Microsoft and other IT companies strongly recommend that you stop using SMBv1 in your network.
However, disabling SMBv1 can cause problems with accessing shared files and folders on newer versions of Windows 10 (Windows Server 2016/2019) from legacy clients (Windows XP, Windows Server 2003), third-party OS (Mac OSX 10.8 Mountain Lion, Snow Leopard, Mavericks, old Linux distros), old NAS devices.
If there are no legacy devices left on your network that support only SMBv1, be sure to disable this SMB dialect in Windows.
If you have clients running Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, or other devices that only support SMBv1, they should be updated or isolated.
How to Enable and Disable SMBv1, SMBv2, and SMBv3 on Windows?
Let’s look at ways to enable and disable different SMB versions on Windows. We’ll cover SMB client and server management (they are different Windows components).
Windows 10, 8.1, and Windows Server 2019/2016/2012R2:
Disable SMBv1 client and server:
Disable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName smb1protocol
Disable SMBv1 server only:
Set-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB1Protocol $false
Enable SMBv1 client and server:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName smb1protocol
Enable only SMBv1 server:
Set-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB1Protocol $true
Disable SMBv2 and SMBv3 server:
Set-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB2Protocol $false
Enable SMBv2 and SMBv3 server:
Set-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB2Protocol $true
Windows 7, Vista, and Windows Server 2008 R2/2008:
Disable SMBv1 server:
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters" SMB1 -Type DWORD -Value 0 –Force
Enable SMBv1 server:
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters" SMB1 -Type DWORD -Value 1 –Force
Disable SMBv1 client:
sc.exe config lanmanworkstation depend= bowser/mrxsmb20/nsi
sc.exe config mrxsmb10 start= disabled
Enable SMBv1 client:
sc.exe config lanmanworkstation depend= bowser/mrxsmb10/mrxsmb20/nsi
sc.exe config mrxsmb10 start= auto
Disable SMBv2 server:
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters" SMB2 -Type DWORD -Value 0 -Force
Enable SMBv2 server:
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters" SMB2 -Type DWORD -Value 1 –Force
Disable SMBv2 client:
sc.exe config lanmanworkstation depend= bowser/mrxsmb10/nsi
sc.exe config mrxsmb20 start= disabled
Enable SMBv2 client:
sc.exe config lanmanworkstation depend= bowser/mrxsmb10/mrxsmb20/nsi
sc.exe config mrxsmb20 start= auto
You can disable SMBv1 server on domain joined computers by deploying the following registry parameter through the GPO:
- Key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters
- Name: SMB1
- Type: REG_DWORD
- Value: 0
Set the registry parameter SMB2=0 in order to disable the SMBv2 server.
To disable the SMBv1 client, you need to propagate the following registry setting:
- Key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\mrxsmb10
- Name: Start
- Type: REG_DWORD
- Value: 4
20 comments
your post save my day!!! thank u, i’m gonna reference it on my blog!!!
I have looked everywhere on the web to resolve this issue. THANK YOU!
Thank you! Got this issue after patching and it worked fine.
Thank you! Saved my day!
How come I have a windows server 2012 r2 with smb1 installed but not visible in dependencies and I can still access it from windows server 2003 ?
If SMB1 diver is running, you can access Windows 2012 R2 from 2003 client:
sc query mrxsmb10
E_NAME: mrxsmb10
TYPE : 2 FILE_SYSTEM_DRIVER
STATE : 4 RUNNING
You don’t need dependency with smb v1, so only v2 is enable in lan manager : this is more secure
`
echo Check SMB protocoles :
echo —————————————
echo.
for %%V in (1 2) do (
for /F %%L in (‘sc qc lanmanworkstation ^| find “mrxsmb%%V0″‘) do (
echo – Lan manager depends of SMB V%%V
for /F %%S in (‘sc query mrxsmb%%V0 ^| find /C “RUNNING”‘) do (
IF %%S EQU 1 (
echo OK, SMB V%%V service is running
) else (
echo.
echo ********************************************************************************************************
echo SMB V%%V is not running, script is ending
echo Type these commands as administrator :
echo.
echo C:^> sc qc lanmanworkstation ^(to show dependances, mrxsmb10 = SMB V1, mrxsmb20 = SMB V2^)
echo C:^> sc config lanmanworkstation depend= bowser/mrxsmb20/nsi ^(In order to disable SMB V1^)
echo C:^> sc config mrxsmb10 start= disabled
echo C:^> sc config mrxsmb20 start= auto ^(to start SMB V2 with system^)
echo Then restart computer
echo ********************************************************************************************************
goto END_SCRIPT
)
)
)
)
`
2012 onwards;
Check it’s not disabled via Powershell too:
To Check:
Get-SmbServerConfiguration | Select EnableSMB1Protocol,
If it say ‘False ‘then Ennable:
Set-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB1Protocol $false
Thank you for your comment. Indeed, SMB1 server protocol is available by default on Windows Server 2012 R2. I updated the article
Perfect, just what the doctor ordered. Saved my life and time.
If you are disabling/removing the SMB1 protocol then you need to make the necessary changes in the registry by enabling the dependencies of SMB 2.0 in Windows Server 2012 R2 through the registry otherwise your shares will stop working. Go to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer and change the value of DependOnService parameter from SamSS Srv to SamSS Srv2. Need to restart the server after this change.
Thanks
Great articles, but you might want to include a reference to the following group policies:
– “Network security: LAN Manager authentication level” change to Send LM & NTLM responses
– “Network security: Minimum session security for NTLM SSP based (including secure RPC) servers “ – Disable Require 128-bit encryption option
– “Network security: Minimum session security for NTLM SSP based (including secure RPC) clients “ – Disable Require 128-bit encryption option
In my case crucial to make it work (win2012 r2)
You the best!! always your posts are rich and very clear to understand!!
Many thanks!!
Thank you man !! very usefull and clear guide in Windows smb labirint.. your detailed instruction work !! i just connected an smb1 printer on 2012 r2.
[…] How to Check, Enable or Disable SMB Protocol Versions on Windows? | Windows OS Hub (woshub.com) […]
Your article says:
This command returned that the SMB1 protocol is disabled (EnableSMB1Protocol = True), and the SMB2 and SMB3 protocols are enabled (EnableSMB1Protocol = False).
But the value of EnableSMB1Protocol is actually *False* and the value of *EnableSMB2Protocol* is True
Unless I’m mistaken, your explanation is topsy-turvy
Great article. Howver, I get different results using diffrent commands. Perhaps I am misisng something
1. sc.exe query mrxsmb10
Error which means does not exist which indicates SMB is not running
2. Sc.exe query mrxsmb20 is running.
3. Get-Item HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters
I get no SMB keys and you state this means SMBv1 amd SMBc2 are enabled by default
4. Gwt-WindowsFeature *smb*
Shows SMB is not installed
5. Get-smbServerConfiguration | select enableSMBProtocol, EnableSMB2Protocl | ft -autosize
EnableSMB1Protocol = True
However,
DISM /online /get-feature /format:table find “SMB1Protocol” returns EnableSMB1Protocol =Disabled.
DISM is accurate.
I feel the most reliable command is the one you mention below:
Hello can you guide me how to enable SMB3 on windows server 2019 please. (server-side)
Domain controllers 2012 R2 have SMB1 disabled by default.
To enable SMB 1.0 support in Windows Server 2012 R2, open the Registry Editor, go to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer and change the value of DependOnService from SamSS Srv2 to SamSS Srv.