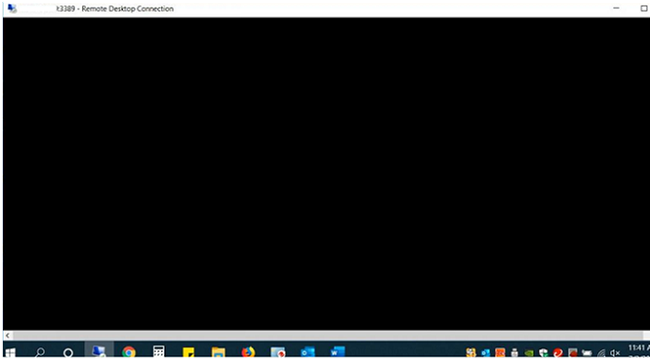
In this article, we will show what to do if you see a black screen instead of a desktop when you connect to a remote Windows host via RDP. This problem often occurs in the latest Windows 10 and Windows Server 2019 builds, and I decided to provide some information about typical solutions from our internal HelpDesk knowledge base.
So you are trying to connect to a remote computer using a standard Windows RDP client (mstsc.exe) and after entering your credentials you see a black screen instead of a desktop.
There are a lot of reasons why a black screen appears in an RDP session. It is quite hard to diagnose or categorize them.
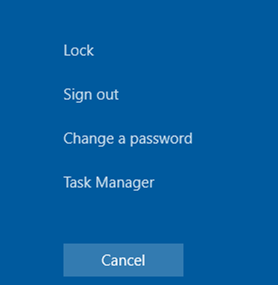
- Press
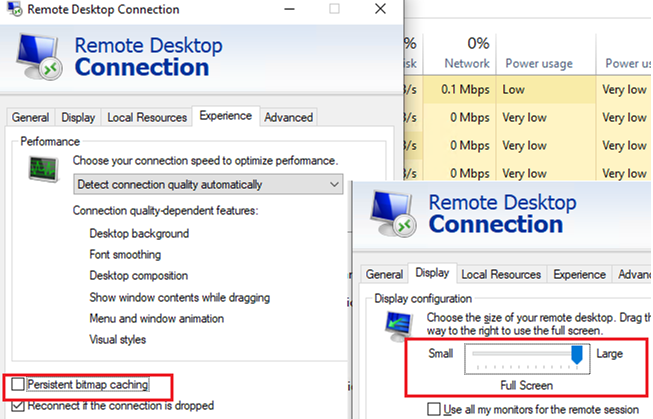
CTRL+ALT+ENDin your RDP session (this also allows you to change a password in your RDP session) and then click Cancel. This sometimes allows you to get back to a desktop in an RDP session. If this doesn’t help, open the Task Manager from this screen and run the File Explorer process (File -> Run new task ->explorer.exe-> OK); - Make sure that caching is disabled in the RDP client settings (disable the Persistent bitmap caching option on the Experience tab) and the screen resolution supported by the remote host is used (set lower screen resolution in the Display tab or try to use the Full Screen mode);
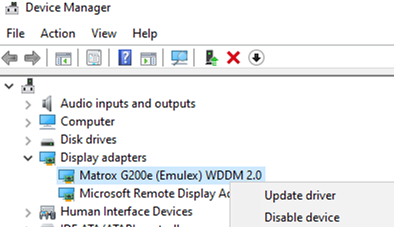
- Make sure that both your computer and the remote one are using the latest video driver versions. Try to use automatic driver update (if you have not disabled it, or download and install the driver manually);
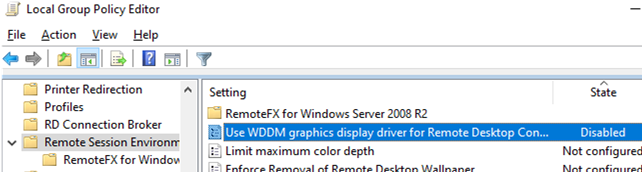
In some cases, you must set using XDDM video driver instead of the WDDM one. To do it, open the Local Group Policy Editor (gpedit.msc) and set Use WDDM graphics display driver for Remote Desktop Connections = Disabled in Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Remote Desktop Services -> Remote Desktop Session Host -> Remote Session Environment (or the same in the registry:reg add “HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows NT\Terminal Services” /v “fEnableWddmDriver” /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f). Update the Group Policy settings on your RDP/RDS host; - In Windows Server 2016 with configured RDP session timeouts, I came across user complaints that after trying to connect to a disconnected session it didn’t activate correctly and they saw a black screen. Only a user can end up their RDP session (
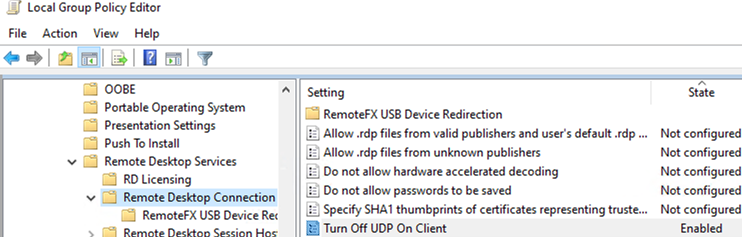
CTRL+ALT+End-> Sign out) or an administrator can forcefully close it (like it is described in the article Remote Desktop Services Is Currently Busy). Or configure more aggressive settings to terminate disconnected user sessions; - Disable using of UDP port 3389 for RDP traffic (it is used together with the default RDP TCP Port 3389 on Windows Server 2012 R2/Windows 8.1 and newer). This can be done by enabling the Turn off UDP on client option in local GPO on the client device (Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Remote Desktop Services -> Remote Desktop Connection Client) or through the registry:
reg add “HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows NT\Terminal Services\Client” /v “fClientDisableUDP” /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f. To disable UDP protocol for the RDP traffic on the server-side, enable the GPO parameter …Remote Desktop Session Host -> Connections -> Select RDP transport protocols =Use only TCP; - Sometimes on RDS hosts, it is necessary to restart the
Audiosrv(Windows Audio) service, after which the user profile is loaded and the Desktop appears.
Microsoft offers some other recommendations that do not always help, but can fix the source of the problem:
- Make sure that your RDP host, client, and all network equipment between them are configured for the same MTU size;
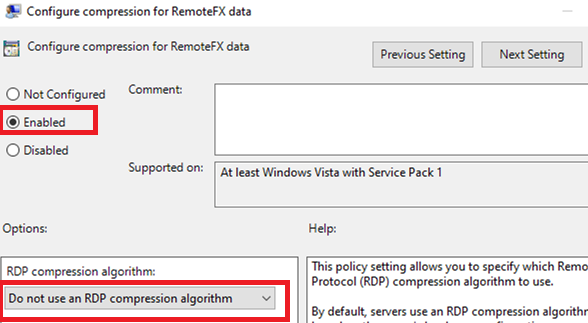
- Disable RDP traffic compression in the local GPO editor: Configure compression for RemoteFX data =
Do not use an RDP compression algorithm(Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Remote Desktop Services -> Remote Desktop Session Host); - If the problem of a black screen in an RDP session occurs on Windows Server 2019 or Windows 10 1809+, open the Event Viewer and check Application and Service Logs –> Microsoft –> Windows –> RemoteDesktopService-RdpCoreTS. See if there are any errors like
‘Failed GetConnectionProperty’ in CUMRDPConnection::QueryProperty at 2884 err=[0x80004001]‘,‘Connection doesn’t support logon error redirector’ in CUMRDPConnection::GetLogonErrorRedirector at 4199 err=[0x80004001]. If you see them, disable the URCP (Universal Rate Control Protocol) used to transfer some data between your RDP client and a server over UDP (MS-RDPEUDP2):
reg add “HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Terminal Server Client” /v “UseURCP” /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f
Or you can set this registry parameter using PowerShell:
New-ItemProperty 'HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Terminal Server Client' -Name UseURCP -PropertyType DWord -Value 0
1 comment
Things I’ve tried:
Disabled RemoteFX
Disabled UDP protocol (via both “Turn Off UDP On Client” and “Select RDP transport protocols”)
Disabled WDDM driver
Disabled the URCP (Universal Rate Control Protocol)
Reduced color-bit depth
Updated graphics drivers to current
Set physical graphics adapter to use “Microsoft Basic Display Adapter”
Disabled Windows Firewall
Nothing seems to resolve the situation.