You can use RDS Drain Mode to maintain terminal hosts in a Remote Desktop Services farm. If you enable Drain Mode for your RDS server, you can prevent the server from accepting new user’s RDP connections, and current RD connections will stay active till users log off manually or automatically by the RDS session timeout. Then you will be able to maintain your Windows Server host without interrupting your RDS farm operation (install updates, change server or app settings, update configuration files, etc.).
What Is Drain Modes on Windows Server Remote Desktop Services?
The Drain Mode appeared in Windows Server 2008 (Terminal Services Server Drain mode). When you put an RDS host in drain mode, it can no longer accept new user’s connections. As a rule, the mode is used when a server administrator needs to maintain a server (install Windows updates, configure or update apps) without affecting the availability of the entire RDS farm. An RDS host can work in either of the three types of the Drain Mode:
- Allow All Connections (a default mode) — an RD Session Host accepts new connections;
- Allow Reconnections, but Prevent New Logons — users are allowed to reconnect to existing sessions, but new sessions are not allowed. If you restart a server, users won’t be able to connect to it;
- Allow Reconnections, but Prevent New Logons until the Server Is Restarted – this mode is similar to the previous one, but after the restart, the user logon mode is reset to Allow All Connections.
How to Deny New User Logons to an RD Session Server?
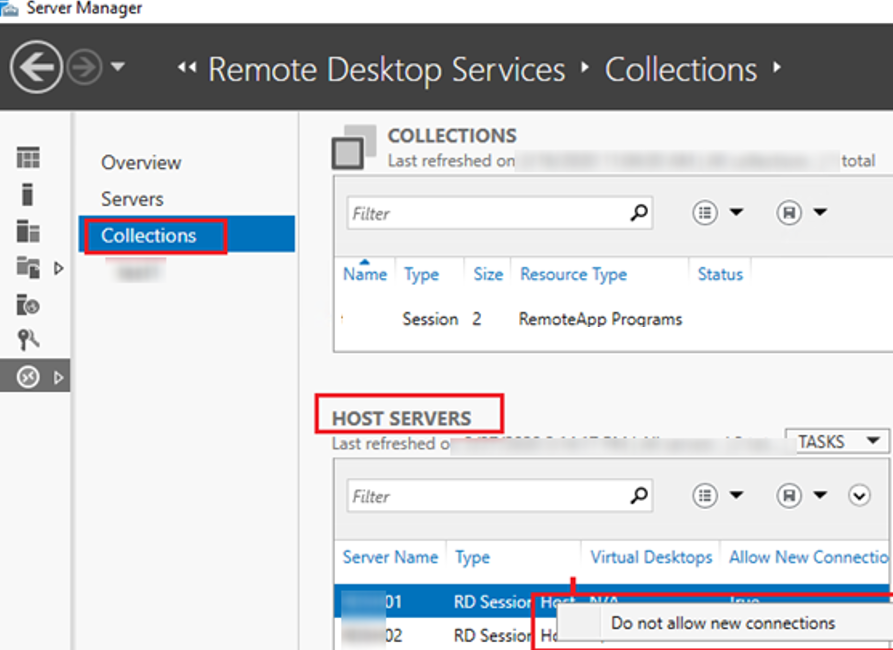
You can enable the Drain Mode on your RDS host server via the RDS collection settings.
- Open Server Manager -> All Servers -> and add all RDS servers of the farm;
- Select Remote Desktop Services on the left panel in the Server Manager. Select the RDS Collections;
- In the
HOST SERVERSsection, select a server you want to enable the Drain Mode for and select Do not allow new connections in the context menu.
Users having active Remote Desktop sessions will be able to reconnect to the server, while all new connections will be forwarded by the RD Connection Broker to other hosts in your RDS farm.
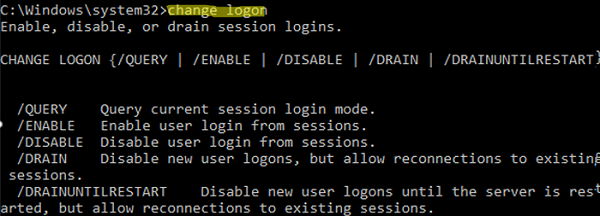
You can also set the Drain Mode locally on the RDS host via the command prompt. To do it, the change logon command is used.
To prevent new user connections, run the command below:
change logon /drain
New user logons are DISABLED, but reconnections to existing sessions are ENABLED
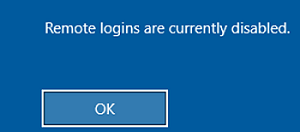
Now, if a new user tries to connect to the RDS host directly (when the RD Connection Broker is not used), the following error appears:
Remote logins are currently disabled.
At the same time an event with the Event ID 1070 and TerminalServices-RemoteConnectionManager as the source appears in the RDS host log:
A logon request was denied because the RD Session Host server is currently in drain mode and therefore not accepting new user logons. To configure the server to allow new user logons, use the Remote Desktop Services Configuration tool.
The following command enables the Drain Mode until the host restart:
change logon /drainuntilrestart
To prevent users even with active sessions to connect to the host, run this command:
change logon /disable
Session logins are currently DISABLED
mstsc /admin).To allow connections, use this command:
change logon /enable
To make sure if the Drain Mode is enabled on your RDS server, run the command below:
change logon /query
Session logins are currently ENABLED
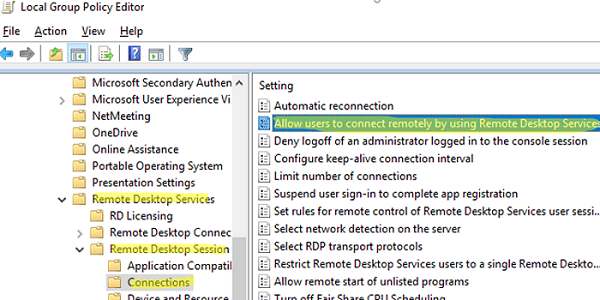
If you tried to set the Drain Mode on your server using change logon and see the following error:
Connections are currently ENABLED by Group Policy for this machine, unable to change.
This means that the Drain Mode is configured via the GPO. The policy setting is called Allow users to connect remotely using Remote Desktop Services and you can find it under the following GPO section: Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Remote Desktop Services -> Remote Desktop Session Host -> Connections.
Disable the policy or set it to Not Configured.
Set Drain Mode for Windows Server RDS Host via PowerShell
You can manage Drain Mode settings of an RDS host collection or a standalone RDS server using PowerShell:
Import-Module RemoteDesktop
# To deny new RDP connections to the Remote Desktop Services Host
Set-RDSessionHost -SessionHost mun-saprdsh1.woshub.com -NewConnectionAllowed No -ConnectionBroker mun-saprdcb.woshub.com
# To allow connections
Set-RDSessionHost -SessionHost mun-saprdsh1.woshub.com -NewConnectionAllowed Yes -ConnectionBroker mun-saprdcb.woshub.com
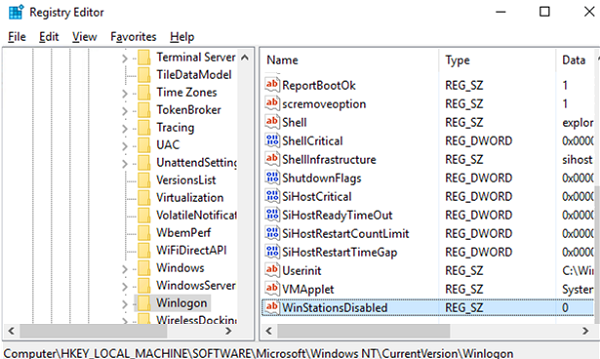
- WinStationsDisabled HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\
- TSServerDrainMode HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\
For example, when the Drain mode is enabled, the registry values are set to WinStationsDisabled = 0 and TSServerDrainMode = 2.
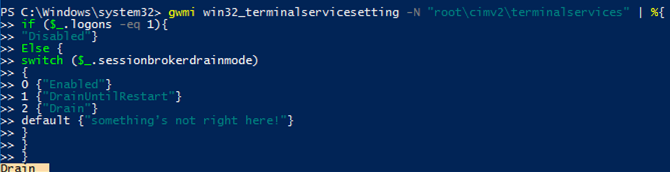
You can also make sure if the Drain Mode on your host is enabled using the PowerShell script below:
Get-WmiObject win32_terminalservicesetting -N "root\cimv2\terminalservices" | %{
if ($_.logons -eq 1){
"Disabled"}
Else {
switch ($_.sessionbrokerdrainmode)
{
0 {"Enabled"}
1 {"DrainUntilRestart"}
2 {"Drain"}
default {"error"}
}
}
}
To enable the Drain Mode via PowerShell (similar to change logon /Drain):
$temp = (Get-WmiObject win32_terminalservicesetting -N "root\cimv2\terminalservices")
$temp.sessionbrokerdrainmode=2
$temp.put()
To put the RDS host to normal mode (change logon /enable), run this command:
$temp = (Get-WmiObject win32_terminalservicesetting -N " root\cimv2\terminalservices ")
$temp.sessionbrokerdrainmode=0
$temp.logons=0
$temp.put()



2 comments
Amazing. I have not hear about this option.
Thank you mate!
Disabling logons on a server locally doesn’t not update the Allow Logins flag on the broker. This is a server-based setting, not collections-based. This does give a more friend, “Remote logins are currently disabled” compared to the broker method which presents an error saying “There are no available computers in the pool. Try connecting again or contact your network administrator”.
They have the same effect though – no logins.